Most website owners unknowingly block search engines from indexing their most valuable content. A single misplaced line in your robots.txt file can tank your organic traffic overnight. Recent data shows that 37% of websites contain robots.txt errors that harm their search visibility.
Understanding how robots.txt works gives you direct control over what search engines see on your site. This powerful text file tells crawlers which pages to access and which to ignore. Smart configuration can dramatically improve your crawl budget and overall rankings.
This guide covers everything you need to master robots.txt for SEO success. You’ll learn proper syntax, common use cases, testing methods, and real world examples. Whether you’re protecting sensitive content or maximising crawl efficiency, you’ll find actionable strategies here.
Drip Ranks specialises in technical SEO implementations that drive measurable results. Our team helps businesses optimise their robots.txt files to improve crawl efficiency and search visibility.
What Is Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a plain text file placed in your website’s root directory that communicates with search engine crawlers. The file uses simple directives to allow or disallow bot access to specific pages, directories, or file types. Every major search engine respects these instructions when crawling your site.
This file serves as your first line of communication with search bots like Googlebot, Bingbot, and others. Crawlers check for robots.txt before accessing any other page on your domain. The file follows the Robots Exclusion Protocol, an internet standard since 1994.
A properly configured robots.txt file appears at yoursite.com/robots.txt and uses straightforward command syntax. Even beginners can create and modify this file without coding knowledge. The format consists of user agent declarations followed by allow or disallow rules.
Why Robots.txt Matters for SEO
Search engines allocate limited crawl budget to each website based on authority and technical health. Understanding what is SEO helps explain why wasting crawl budget on low value pages means fewer high priority pages get indexed quickly. Robots.txt helps you direct crawler attention to your most important content.
Blocking duplicate content, admin pages, and resource files prevents index bloat and potential ranking issues. Sites with thousands of thin or duplicate pages risk diluting their ranking signals. Strategic blocking keeps your index clean and focused on revenue generating pages.
Proper robots.txt configuration protects sensitive information from appearing in search results before you’re ready. Staging environments, internal search results, and parameter heavy URLs often create crawl traps. Blocking these URLs saves bandwidth and prevents user experience issues.
How Robots.txt Works
When a search crawler arrives at your domain, it immediately requests the robots.txt file from the root directory. The crawler reads all directives applicable to its user agent before proceeding to crawl other pages. If no robots.txt file exists, crawlers assume full access to all content.
The file operates on a hierarchical matching system where specific rules override general ones. A user agent directive identifies which bot the following rules apply to, such as Googlebot or Bingbot. Rules remain in effect until the next user agent declaration appears.
Crawlers cache your robots.txt file and typically check for updates every 24 hours. Changes to your file may take a full day to affect crawler behavior across your site. Testing changes before deployment prevents accidentally blocking critical pages from indexation.
Essential Robots.txt Syntax and Commands
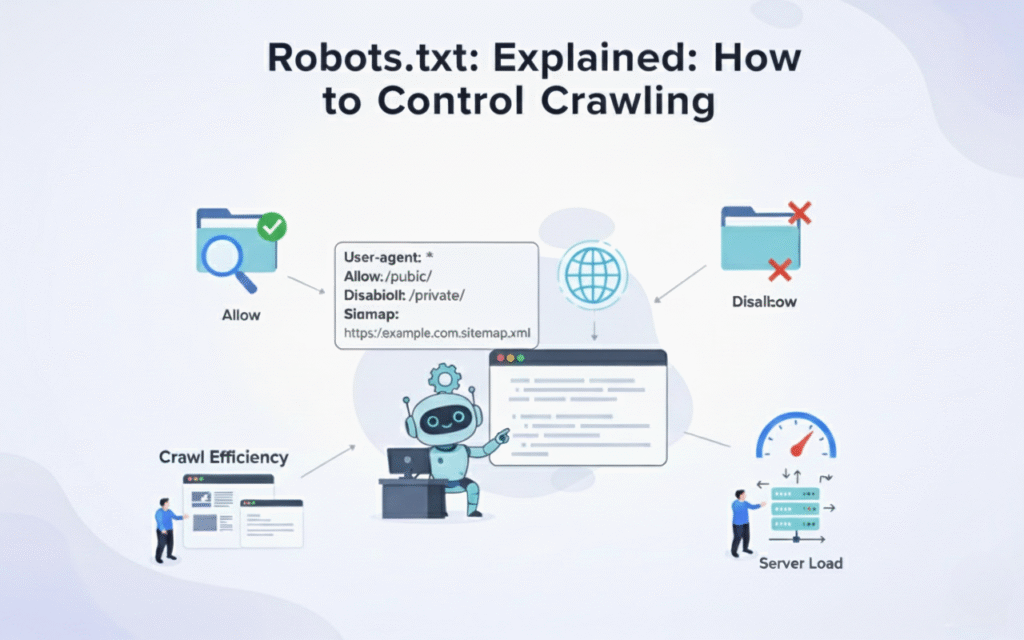
The User agent directive specifies which crawler the following rules apply to, using asterisk for all bots. For example, “User agent: ” applies rules universally while “User agent: Googlebot” targets only Google’s crawler. Always place this directive before any allow or disallow rules.
The Disallow command blocks crawlers from accessing specified paths, directories, or file patterns. “Disallow: /admin/” prevents access to your entire admin directory and all subdirectories beneath it. Leaving a disallow line empty grants full access to that user agent.
The Allow directive explicitly permits access to paths that might otherwise be blocked by broader rules. This command proves useful when you want to disallow a directory but allow specific files within it. Most modern crawlers support allow directives, though older bots may ignore them.
The Sitemap directive points crawlers directly to your XML sitemap location for faster discovery. Including “Sitemap: https://yoursite.com/sitemap.xml” helps search engines find and crawl important pages efficiently. You can list multiple sitemaps if your site structure requires it.
Wildcards and special characters extend robots.txt functionality for pattern matching and precise control. The asterisk matches any sequence of characters while dollar sign ($) indicates end of URL. These tools enable sophisticated blocking patterns without listing every individual URL.
Common Robots.txt Use Cases
Blocking duplicate content versions prevents search engines from indexing printer friendly pages, session IDs, or filtered product pages. E-commerce sites often generate thousands of URL variations through faceted navigation and sorting parameters. Disallowing these patterns keeps your index clean and consolidated.
Protecting admin areas, login pages, and internal search results maintains security and prevents wasted crawl budget. These functional pages serve users but provide no SEO value when indexed in search results. Blocking them focuses crawler attention on your customer facing content.
Managing crawl rate for large sites ensures search engines don’t overwhelm your server with requests. Sites with millions of pages need strategic blocking to prevent resource intensive crawling of low priority sections. This approach maintains site performance while ensuring important content gets crawled regularly.
Preventing indexation of staging and development environments stops incomplete content from appearing in search results prematurely. A simple “Disallow: /” on staging servers prevents embarrassing leaks and duplicate content issues. Always verify robots.txt settings before launching new site versions.
Testing Your Robots.txt File
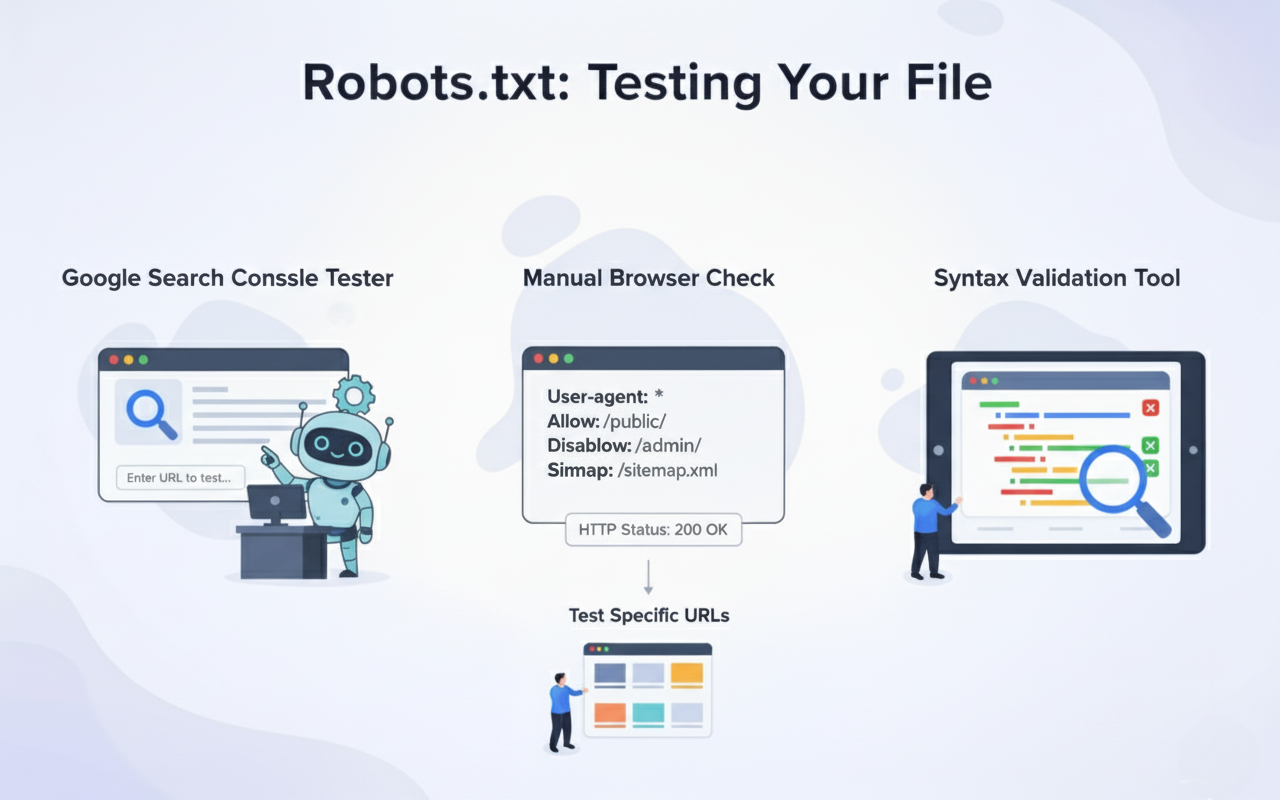
Google Search Console offers a robots.txt Tester tool that shows exactly how Googlebot interprets your file. The tool highlights syntax errors, displays blocked URLs, and lets you test specific URLs against your rules. This free resource prevents costly mistakes before they impact your rankings.
Manual testing involves entering yoursite.com/robots.txt in a browser to verify the file loads correctly. Check that the file returns a 200 status code and displays plain text without HTML formatting. Missing or inaccessible robots.txt files may signal technical issues requiring immediate attention.
Syntax validation tools catch formatting errors that could break your directives or create unintended blocks. Small typos like missing colons or incorrect spacing can render entire sections of your file ineffective. Regular validation ensures your rules function exactly as intended.
Testing specific URLs against your robots.txt rules confirms that blocking patterns work as expected. The Google Tester shows whether a given URL would be allowed or blocked for Googlebot. Run tests on representative URLs from each section of your site before finalising changes.
Robots.txt Best Practices
Keep your robots.txt file simple and well documented with comments explaining each section’s purpose. Use hash symbols (#) to add comments that help future administrators understand your blocking strategy. Clear documentation prevents accidental changes that could harm your search visibility.
Never use robots.txt to hide content you want completely private or secure from public access. Determined users can still access blocked URLs by typing them directly into browsers. Use proper authentication and noindex tags for truly sensitive content.
Regularly audit your robots.txt file as your site grows and evolves to ensure rules remain relevant. Outdated blocking patterns may prevent new valuable content from being discovered and indexed. Schedule quarterly reviews to keep your file aligned with current site structure.
Combine robots.txt with meta robots tags and X Robots Tag headers for comprehensive crawl control. While robots.txt blocks crawling, noindex tags prevent indexing of already crawled pages. This layered approach gives you precise control over search engine interaction.
Monitor crawl stats in Google Search Console to verify that your robots.txt changes produce desired effects. Watch for sudden drops in crawled pages or increases in blocked resources that might indicate problems. Quick detection of issues minimises ranking impact.
Common Robots.txt Mistakes to Avoid
Blocking CSS, JavaScript, or image files prevents Google from fully rendering and understanding your pages. Modern search algorithms rely on complete page rendering to evaluate user experience and content quality. Allow access to all resources necessary for proper page display.
Using robots.txt to control indexing instead of noindex tags creates confusion and potential ranking problems. Blocked pages can still appear in search results if external links point to them. Proper indexing control requires meta robots tags or HTTP headers.
Creating overly complex patterns with excessive wildcards and rules makes maintenance difficult and error prone. Simple, straightforward rules prove easier to test, validate, and update as your site changes. Break complex blocking needs into clear, logical sections.
Forgetting to update robots.txt after site migrations or redesigns often blocks new important content accidentally. URL structure changes may render old blocking patterns ineffective or harmfully broad. Include robots.txt review in every major site update checklist.
Blocking your entire site with “Disallow: /” while working on a live production environment tanks rankings instantly. This common mistake during troubleshooting can take weeks to recover from after correction. Always double check before saving changes to production robots.txt files.
Advanced Robots.txt Strategies
Implementing user agent specific rules allows different treatment for various search engines based on their capabilities. You might allow Google full access while restricting aggressive scrapers or less important bots. This granular control optimises crawl budget distribution across different crawlers and supports clear SEO benefits.
Using crawl delay directives helps manage server load for sites experiencing crawler related performance issues. While Google ignores this directive, other search engines respect crawl delay values to space out requests. Set appropriate delays that balance crawl efficiency with server capacity.
Creating dynamic robots.txt files through server side generation enables sophisticated rules based on user agent or conditions. Large sites with complex requirements can programmatically generate appropriate rules for different scenarios. This approach requires development resources but offers maximum flexibility.
Coordinating robots.txt with log file analysis reveals which bots consume most resources and how they respond to blocking. Regular analysis shows whether your blocking strategies achieve desired crawl budget optimissation. Data driven adjustments improve efficiency over time.
Tools and Resources for Robots.txt Management
Google Search Console provides free robots.txt testing, crawl stats, and indexing reports for comprehensive monitoring. The Coverage report shows which pages Google successfully crawled versus those blocked by robots.txt. These insights guide ongoing optimisation efforts and highlight essential SEO tools.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider crawls your site while respecting robots.txt rules to show exactly what search engines see. The tool identifies blocked resources, crawl depth issues, and orphaned pages needing attention. Desktop and cloud versions handle sites of all sizes.
Online robots.txt generators help beginners create properly formatted files without syntax errors. These tools provide templates for common scenarios and validate output before deployment. While useful for learning, customise generated files to match your specific needs.
Technical SEO platforms like Sitebulb, DeepCrawl, and Botify offer advanced robots.txt analysis within comprehensive site audits. These enterprise tools correlate blocking patterns with crawl behavior, rankings, and indexation issues. Investment makes sense for large, complex websites.
Robots.txt and Site Architecture
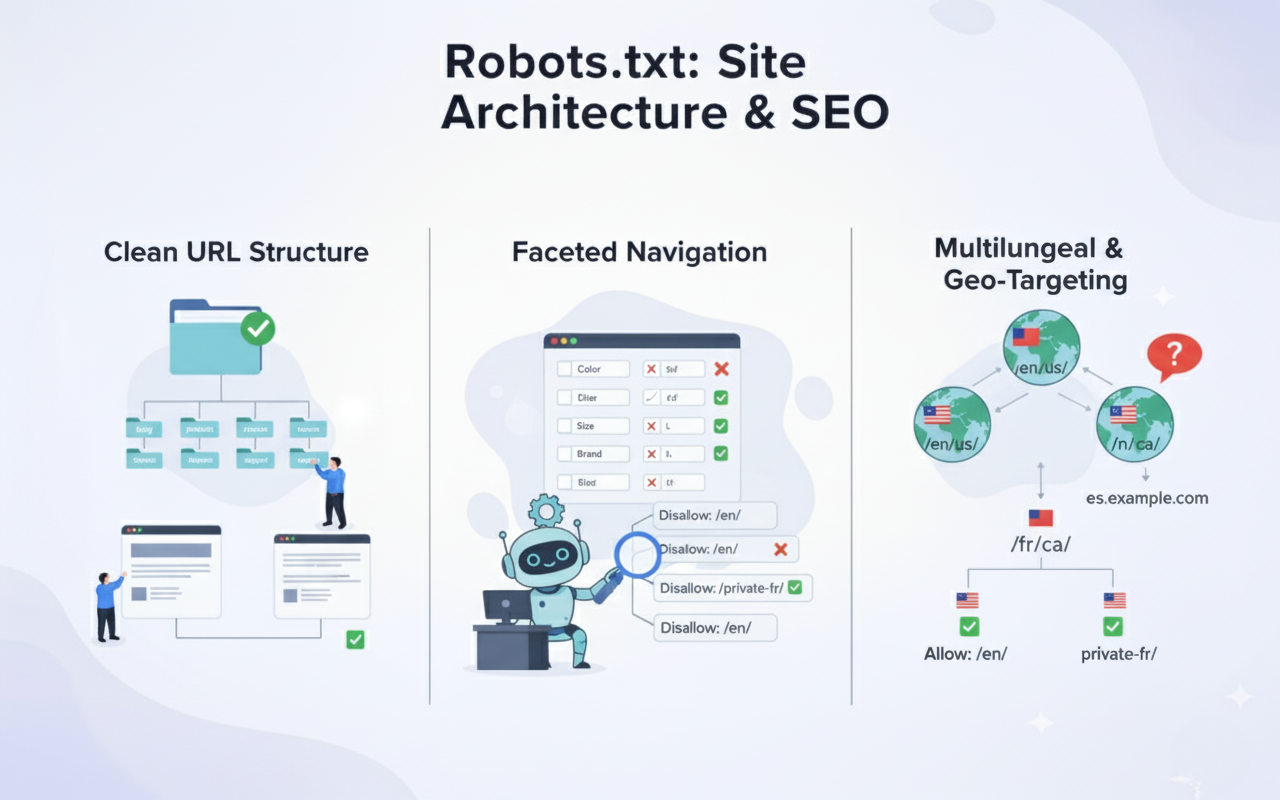
Organising your site hierarchy logically makes robots.txt rules simpler and more maintainable over time. Clean URL structures with clear directory patterns allow straightforward blocking of entire sections. Poor architecture requires complex pattern matching prone to errors.
Implementing faceted navigation requires careful robots.txt planning to prevent parameter explosion in your index. Block filter combinations that create duplicate content while allowing individual facets to be crawled. Balance user experience needs with technical SEO requirements.
Managing multilingual and multi regional sites through robots.txt requires consideration of subdirectories, subdomains, or separate domains. Each structure type demands different blocking approaches to avoid accidentally blocking language or region variations. Document your approach clearly for consistent implementation.
Future of Robots.txt and Crawl Control
Google continues evolving its understanding of JavaScript and modern web technologies beyond basic robots.txt rules. The search engine now renders pages more like browsers, accessing some resources regardless of blocking. Staying current with crawler capabilities ensures your strategies remain effective.
Increasing focus on Core Web Vitals and page experience means resource blocking carries additional ranking implications. Blocking critical rendering resources can harm performance scores even if your content gets indexed. Balance blocking with performance optimisation goals.
Alternative crawl control methods like IndexNow protocol and API based indexing may supplement traditional robots.txt approaches. These technologies enable real time communication with search engines about content changes. Forward thinking SEO strategies incorporate multiple signaling methods.
Final Words
Most SaaS, B2B, and agency teams treat robots.txt like a technical formality: add a file, hope crawlers behave, and wonder why rankings aren’t predictable. At Drip Ranks, we knew there had to be a better way. So we built a system, not a service.
Forensic audits uncover your highest ROI opportunities, showing exactly where robots.txt optimisations can improve crawl efficiency, protect your most valuable pages, and prevent duplicate content issues. Intent-mapped strategies ensure every technical adjustment supports the buyer journey, while scalable execution multiplies results without increasing headcount. The difference? Your SEO becomes measurable, repeatable, and revenue-focused, not a black box that relies on guesswork.
Drip Ranks delivers expert technical SEO services that maximise search performance. Our team audits, optimises, and monitors your robots.txt configuration to ensure flawless crawler communication. Contact us today to boost crawl efficiency and unlock your site’s full ranking potential.