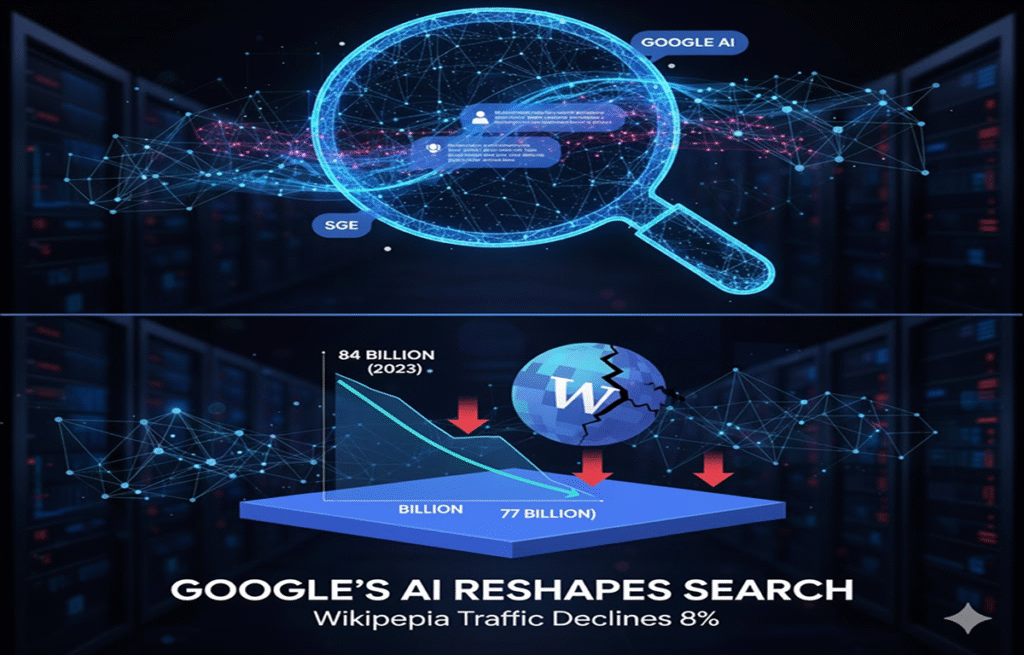
Google’s AI-powered search features are reshaping how users find information online
Wikipedia has recorded an 8% decline in global traffic, marking a significant shift in how internet users access information. The drop comes as Google’s AI-powered search features, including Search Generative Experience (SGE) and featured snippets, increasingly answer user queries directly on search results pages.
The world’s largest online encyclopaedia saw its traffic fall from 84 billion visits in 2023 to approximately 77 billion in 2024, according to recent analytics. This decline signals a broader transformation in search behaviour that digital marketers and SEO professionals cannot ignore.
Why Wikipedia’s Traffic Decline Matters for SEO
Wikipedia has long dominated Google’s first page for informational queries. Its decline reveals how AI-generated overviews and zero-click searches are fundamentally changing organic search dynamics.
When users get instant answers from Google’s AI summaries, they no longer need to click through to source websites – even authoritative ones like Wikipedia. This trend affects all content publishers, from small businesses to major media outlets.
The geographic distribution of traffic losses varies considerably. Regions with higher AI feature adoption show steeper declines, whilst markets with limited SGE rollout maintain more stable Wikipedia traffic patterns.
What This Means for Your Content Strategy
Search engine optimisation is no longer just about ranking first. It’s about appearing in AI-generated answers, featured snippets, and knowledge panels that keep users within Google’s ecosystem.
Content creators must adapt by focusing on:
- Entity-based SEO – Structuring content around clear topics and entities that AI can easily parse and reference
- Featured snippet optimisation – Formatting answers concisely to appear in position zero results
- E-E-A-T signals – Demonstrating expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness to compete with established sources
- Conversational keywords – Targeting natural language queries that users ask AI assistants
Traditional keyword strategies that worked five years ago now deliver diminishing returns. The focus has shifted to semantic relevance and topical authority.
The Rise of Zero-Click Searches
Industry data shows that over 60% of Google searches now end without a click to an external website. Users find what they need directly in search results through AI overviews, featured snippets, and knowledge graphs.
This zero-click trend accelerates as Google’s AI features become more sophisticated. The search giant’s Gemini integration provides increasingly comprehensive answers without requiring users to visit source websites.
For businesses, this means traditional traffic metrics need re-evaluation. Visibility in AI-generated answers may matter more than click-through rates in certain contexts.
Expert Analysis: Adapting to AI-First Search
The Wikipedia traffic drop serves as an early warning for all digital publishers. If one of the internet’s most authoritative sources experiences an 8% decline, smaller sites face even greater challenges.
Smart SEO strategies now require diversification. Relying solely on organic Google traffic creates vulnerability to algorithmic changes and AI feature updates. Successful brands invest in multiple channels including social media, email marketing, and direct traffic sources.
Geographic targeting also gains importance. Markets with lower AI adoption rates still offer traditional SEO opportunities, whilst mature markets demand AI-optimisation tactics.