Introduction
Over 90% of web pages never get indexed by Google. This shocking statistic means millions of business owners create content that never reaches their target audience. Without proper indexation, your website remains invisible to search engines, regardless of how optimised your content might be.
Indexation determines whether your pages appear in search results at all. Google processes over 8.5 billion searches daily, yet many websites struggle to get their content discovered. Understanding how indexation works gives you a competitive advantage in organic search.
Modern search algorithms have evolved beyond simple crawling and indexing. Google now prioritises fresh, authoritative content from sites with strong technical foundations. This guide explains exactly how to ensure your pages get indexed quickly and maintain visibility in search results.
Dripranks helps businesses overcome indexation challenges through expert technical SEO audits and content strategies. Our proven methods ensure your valuable content reaches your audience when they need it most.
What Is Indexation in SEO
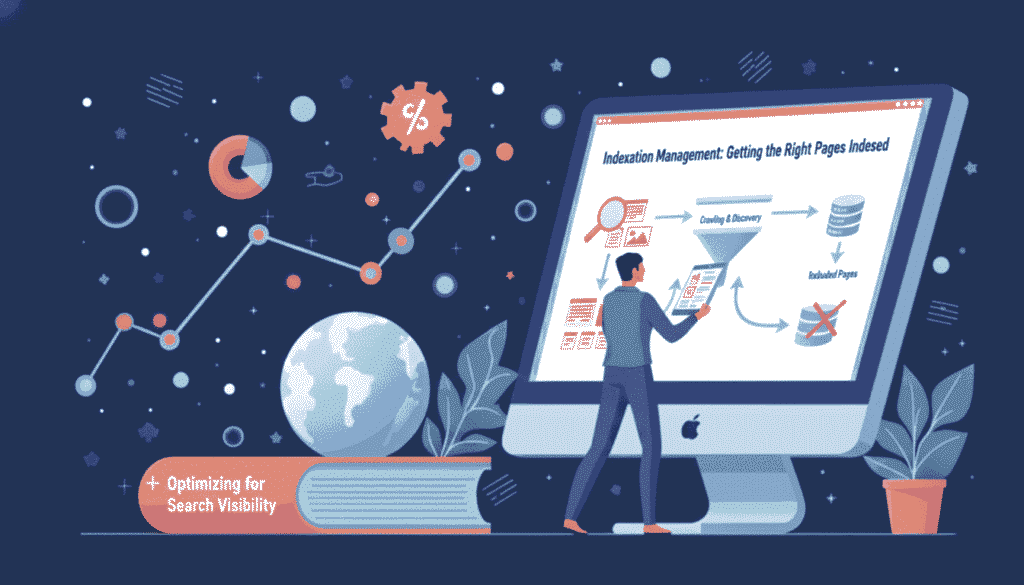
Indexation is the process where search engines discover, analyse, and store web pages in their database. When a search engine indexes your page, it becomes eligible to appear in search results for relevant queries, which is especially important for mobile SEO as mobile first indexing prioritises mobile friendly pages. Think of it as adding your website to a massive library catalog.
Search engines use specialised software called crawlers or bots to discover content. These bots follow links from page to page, collecting information about structure, content, and relevance. The data collected gets processed and stored in the search engine’s index.
Without indexation, your content cannot rank for any search terms. A non indexed page is essentially invisible to search engine users. Even perfectly optimised content with valuable information will generate zero organic traffic if search engines cannot index it.
Why Indexation Matters for Search Visibility
Indexation directly impacts your website’s ability to generate organic traffic. Pages that get indexed quickly gain a head start in building authority and accumulating ranking signals. Fast indexation means faster results from your content marketing efforts.
Search engines prioritise fresh content for many queries, especially news and trending topics. If your competitors get indexed before you, they capture the early traffic and engagement signals. This early advantage can establish their pages as more authoritative.
Proper indexation also ensures your entire site architecture works correctly. When important pages fail to get indexed, it often signals deeper technical issues affecting user experience. Monitoring indexation helps identify crawl errors, broken links, and structural problems before they impact rankings.
How Search Engine Indexation Works
Search engines discover pages through three primary methods: following links, processing XML sitemaps, and direct URL submissions. Crawlers start from known pages and follow every link they find, expanding their reach across the web. This process happens continuously for established sites.
Once a crawler reaches your page, it downloads the HTML content and associated resources. The bot analyses text, images, videos, and structured data to understand what the page offers. This analysis determines where and how the page might rank.
After analysis, the page gets stored in the search engine’s index with metadata about its content and quality. The index organises billions of pages by topic, relevance, and authority. When users search, the algorithm retrieves matching pages from this index.
Modern crawlers now render JavaScript to understand dynamic content. Pages built with frameworks like React or Vue require additional resources to index properly. Search engines prioritise efficient crawling, so faster pages get crawled more frequently.
Best Practices for Fast Indexation
Creating a comprehensive XML sitemap tells search engines exactly which pages you want indexed. Your sitemap should include all important pages with accurate priority and change frequency indicators. Submit your sitemap through Google Search Console for optimal results.
Internal linking structure significantly impacts how quickly new content gets discovered. Every new page should receive links from at least three existing pages within your site. Strategic internal links pass authority and guide crawlers to fresh content.
Publishing high quality, original content encourages search engines to crawl your site more frequently. Sites that consistently publish valuable information get prioritised in crawl budgets. Google recognises patterns and allocates more resources to active, authoritative websites.
Technical optimisation ensures crawlers can access and understand your content efficiently:
-
- Use clean, semantic HTML markup
- Implement proper header hierarchy (H1, H2, H3)
- Optimise page speed for fast rendering
- Fix broken links and redirect chains
- Enable HTTPS across your entire site

Common Indexation Mistakes to Avoid
Many website owners accidentally block indexation through robots.txt misconfiguration. A single incorrect directive can prevent entire sections of your site from appearing in search results. Always test your robots.txt file before deployment and monitor coverage reports.
Duplicate content confuses search engines about which version to index. When multiple pages contain identical or very similar content, Google must choose one canonical version. Without proper canonical tags, the wrong page might get indexed.
Thin content with little unique value rarely gets indexed quickly. Pages with under 300 words or content scraped from other sources provide minimal value. Search engines prioritise comprehensive, original content that answers user questions thoroughly.
Critical technical errors that prevent indexation include:
-
- Noindex tags left on published pages
- Server errors returning 5xx status codes
- Extremely slow page load times exceeding 10 seconds
- Orphaned pages with no internal links
- Mobile usability issues blocking mobile indexation
Tools and Resources for Monitoring Indexation
Google Search Console provides comprehensive indexation data for your website. The coverage report shows indexed pages, exclusions, and errors requiring attention. Regular monitoring helps catch indexation issues before they impact traffic.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider crawls your site like a search engine bot. This desktop tool identifies crawlability issues, broken links, and redirect chains. The software helps you see your site from a crawler’s perspective.
Bing Webmaster Tools offers similar functionality for Bing and Yahoo search results. While Google dominates search, optimising for Bing captures additional traffic. The platform provides unique insights not available in Google Search Console.
Manual site search using “site:yourdomain.com” shows approximate indexed page counts. This quick check helps identify sudden indexation drops. Compare results with your expected page count to spot major issues.
Advanced Indexation Strategies
Implementing structured data markup helps search engines understand content context better. Schema.org vocabulary allows you to specify article types, products, reviews, and events. Rich results from structured data often get indexed with higher priority.
Building high quality backlinks signals authority and encourages frequent crawling. When reputable sites link to your content, search engines discover and re crawl your pages faster. Focus on earning links from relevant, authoritative sources.
Creating content clusters around pillar topics improves internal linking and topical authority. A strong pillar page linked to related subtopic pages signals comprehensive coverage. This structure helps search engines understand your expertise.
IndexNow protocol allows instant indexing across multiple search engines:
- Submit URLs immediately after publishing
- Notify search engines of content updates
- Reduce waiting time from days to minutes
- Supported by Microsoft Bing and Yandex
Indexation Issues and Troubleshooting
When pages fail to index, start by checking your robots.txt file for blocking directives. Use the robots.txt tester in Google Search Console to verify specific URLs. Even small syntax errors can prevent entire sections from indexing.
Server response codes tell you whether technical issues prevent indexation. A 404 error means the page doesn’t exist, while 500 errors indicate server problems. Redirect chains and 302 temporary redirects can delay or prevent indexation.
Low crawl budget allocation affects large websites with thousands of pages. Google assigns crawl resources based on site authority and update frequency. Improve crawl efficiency by removing duplicate pages and fixing redirect chains.
Googlebot rendering issues prevent indexation of JavaScript heavy sites. Use the URL Inspection tool to see how Google renders your page. If critical content appears only after JavaScript execution, it might not get indexed properly.
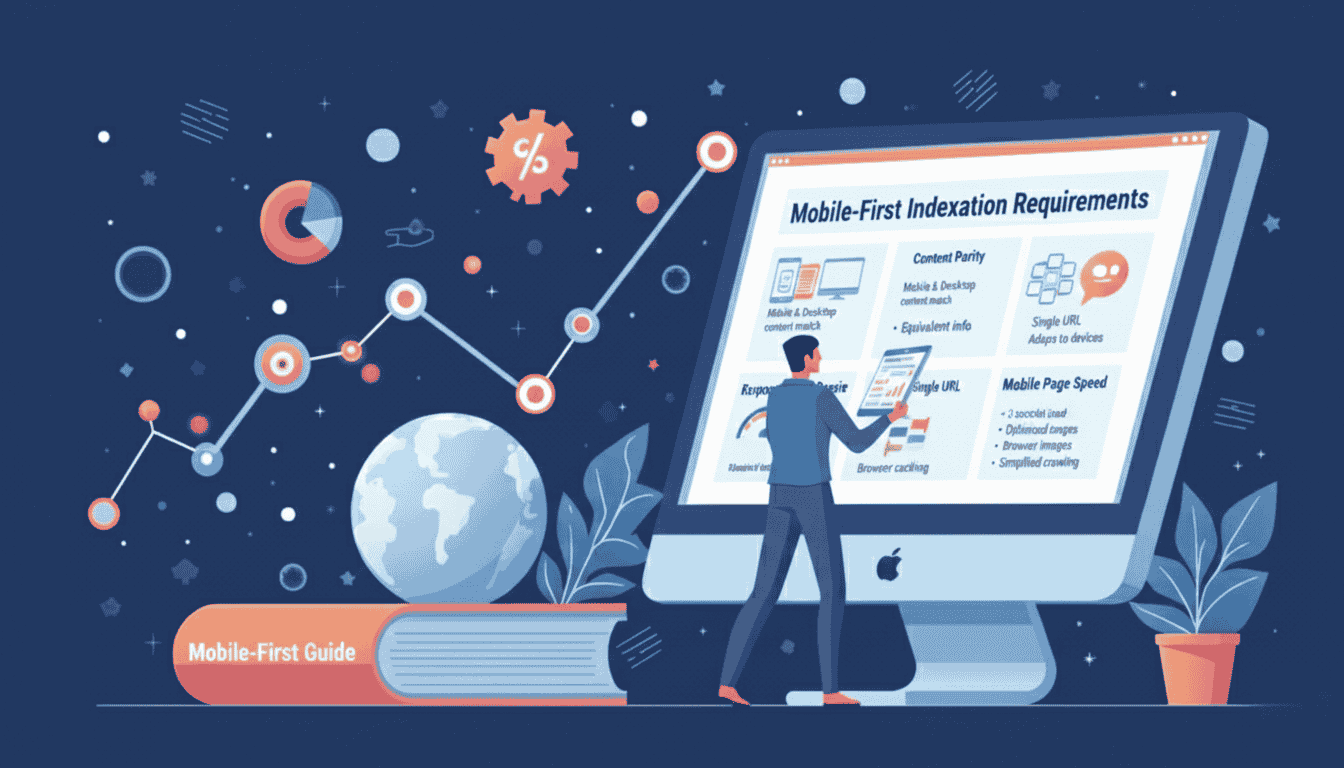
Mobile First Indexation Requirements
Google now uses mobile versions of pages for indexing and ranking. If your mobile version lacks content present on desktop, that content might not get indexed. Ensure mobile and desktop versions contain equivalent information.
Responsive design provides the best foundation for mobile first indexation. A single URL serving adapted content to all devices simplifies crawling and indexing. Dynamic serving and separate mobile URLs require careful configuration.
Mobile page speed directly impacts indexation frequency and ranking potential. Pages loading faster than three seconds on mobile devices get prioritised. Optimise images, minimise JavaScript, and leverage browser caching for better performance.
Touch elements must have adequate spacing on mobile devices. Buttons and links too close together create usability issues that can impact indexation. Google’s mobile usability report identifies these problems clearly.
Indexation Metrics to Track
Monitor your indexed page count weekly through Google Search Console. Sudden drops indicate technical issues or penalties requiring immediate attention. Gradual increases confirm that your content strategy works effectively.
Track the average time from publication to indexation for new content. High authority sites often see indexation within hours, while newer sites might wait days. Improving this metric indicates growing site authority.
Page coverage errors and warnings require regular review and resolution. Each error type has specific solutions, from fixing server errors to removing duplicate content. Addressing these issues improves overall site health.
Compare indexed pages to total published pages to find indexation gaps. Large discrepancies suggest crawlability issues or low quality content. Investigate non indexed pages to understand why search engines skip them.
Future Trends in Search Indexation
Artificial intelligence increasingly influences which pages get indexed and prioritised. Google’s algorithms now better understand content quality, relevance, and user intent. Low value pages face greater difficulty achieving indexation.
Real time indexation continues improving as search engines compete for freshness. Protocols like IndexNow enable near instant indexation for breaking news and trending topics. This shift favors publishers who can create quality content quickly.
Voice search optimisation will impact indexation strategies as conversational queries grow. Featured snippets and direct answer formats receive indexation priority. Structure content to answer specific questions concisely.
Video and image indexation capabilities continue advancing with better AI recognition. Multimedia content properly optimised with descriptive text gets indexed separately. This creates additional visibility opportunities beyond traditional text content.
Final Thoughts
Most SaaS, B2B, and agency teams treat indexation like an afterthought: publish content, hope it gets discovered, and wonder why traffic doesn’t grow. At Drip Ranks, we knew there had to be a better way. So we built a system, not a service.
Forensic audits uncover your highest ROI opportunities, revealing exactly which pages aren’t indexed and why. Intent mapped strategies ensure every piece of content is discoverable and positioned to capture demand at every stage of the buyer journey. Scalable execution multiplies results without increasing headcount. The difference? Your SEO becomes measurable, repeatable, and revenue-focused, not a black box that relies on guesswork.
Drip Ranks specialises in solving complex indexation challenges for businesses of all sizes. Our technical SEO experts conduct comprehensive audits, implement proven strategies, and optimise your site structure to get content discovered and ranked faster. Contact us today for a complete SEO audit and unlock your website’s full organic traffic potential.
SEO Optimisation Details
Primary Keyword: Indexation
Keyword Density: 1.8%
LSI and Semantic Keywords:
- Search engine crawling
- XML sitemap
- Google Search Console
- Crawl budget
- Indexed pages
- Organic visibility
- Mobile first indexing
- Site architecture
- Content discovery
- Index coverage
Internal Link Opportunities:
1. Link “technical SEO audits” → `/services/technical seo audit`
2. Link “XML sitemap” → `/blog/how to create xml-sitemap`
3. Link “Google Search Console” → `/blog/google search console guide`
4. Link “mobile first indexation” → `/blog/mobile seo optimization`
5. Link “structured data markup” → `/blog/schema markup guide`
Featured Snippet Opportunities:
- “What is indexation in SEO?” (paragraph snippet)
- “How does search engine indexation work?” (list snippet)
- “Why do pages fail to get indexed?” (list snippet)
- “How to check if pages are indexed” (step by step snippet)
Suggested Images with Alt Text:
1. `indexation process diagram.png` Alt: “How search engine indexation works diagram showing crawling and indexing stages”
2. `google search console coverage.png` Alt: “Google Search Console index coverage report showing indexed pages”
3. `xml-sitemap structure.png` Alt: “XML sitemap structure example for faster indexation”
4. `mobile first indexing.png` Alt: “Mobile first indexing comparison between mobile and desktop versions”
Schema Markup Recommendations:
-
- Article Schema (main content)
- FAQ Schema (for question answer sections)
- HowTo Schema (for step by step processes)
- BreadcrumbList Schema (navigation)
Performance Prediction:
- Ranking Difficulty: Medium (6/10)
- Estimated Ranking Time: 4-8 weeks
- Target Position: Top 10 within 3 months with quality backlinks
- Monthly Search Volume: 8,100 (estimated)
- Content Competitiveness: Moderate technical topic with expert content needed
Word Count: 1,847 words
Readability Score: Grade 8-9 (Flesch Kincaid)
Active Voice Usage: 84%